Intelligent Features
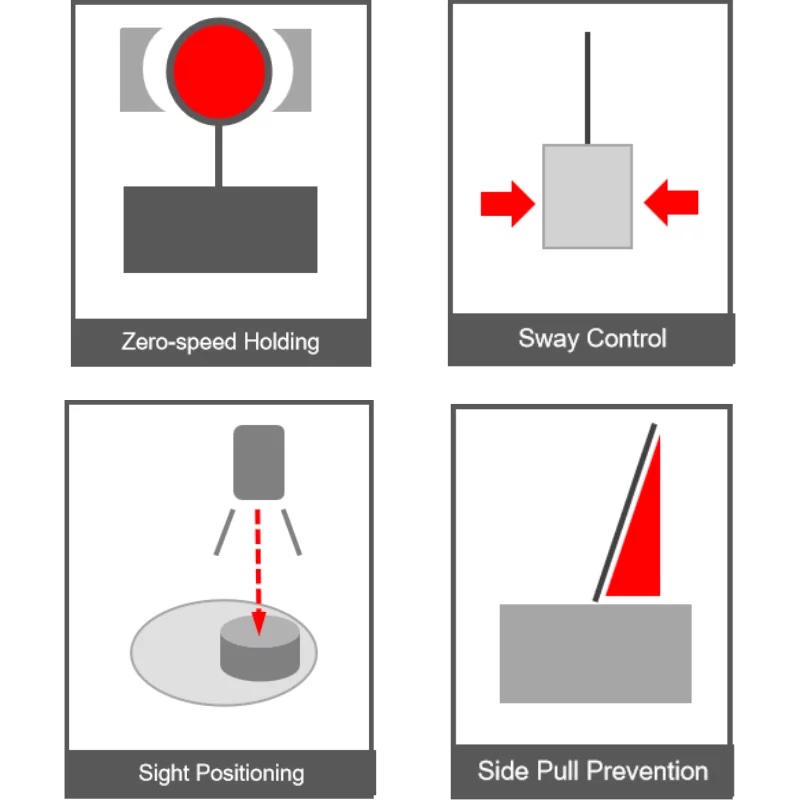
Sway Control
Zero-speed holding
Automatic Positioning
Side Pull Prevention
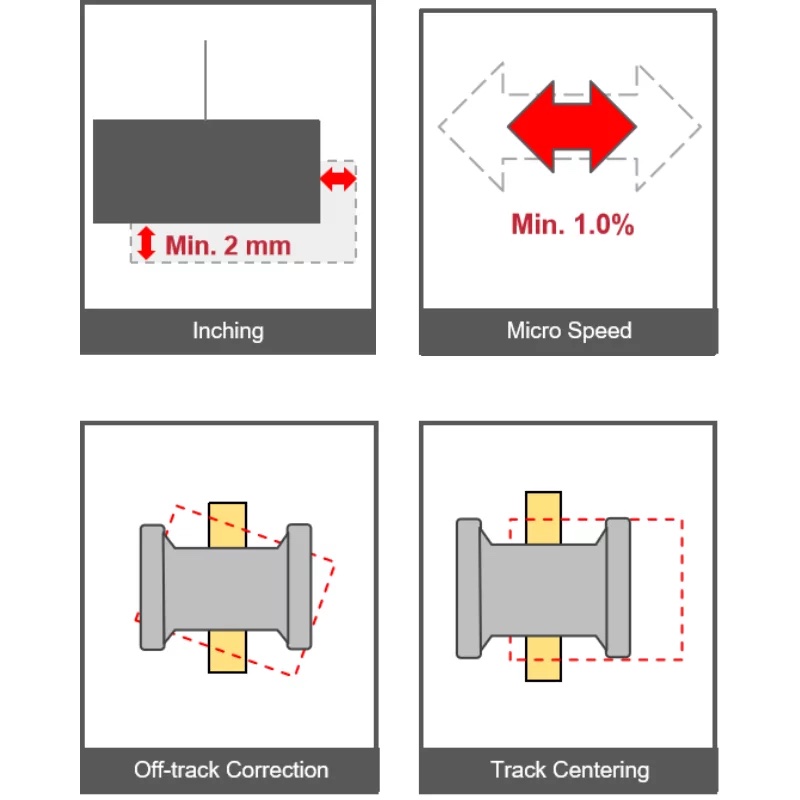
Inching and Micro Speed Control
Off-track Correction
Track Centering
Fault Self-Diagnosis
Shock Load Prevention
Anti-Lock Protection
Zone Protection
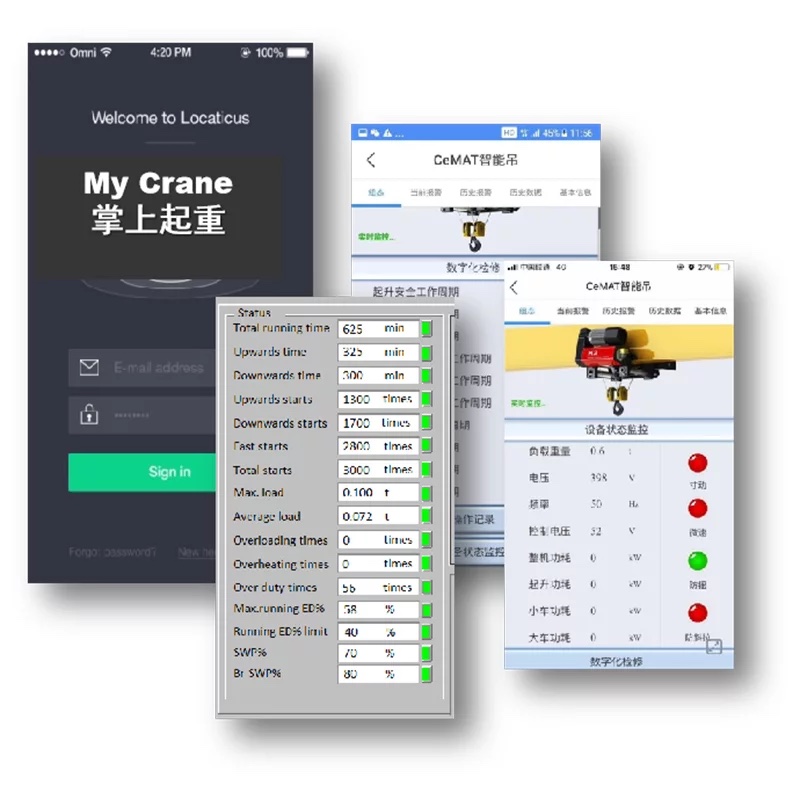
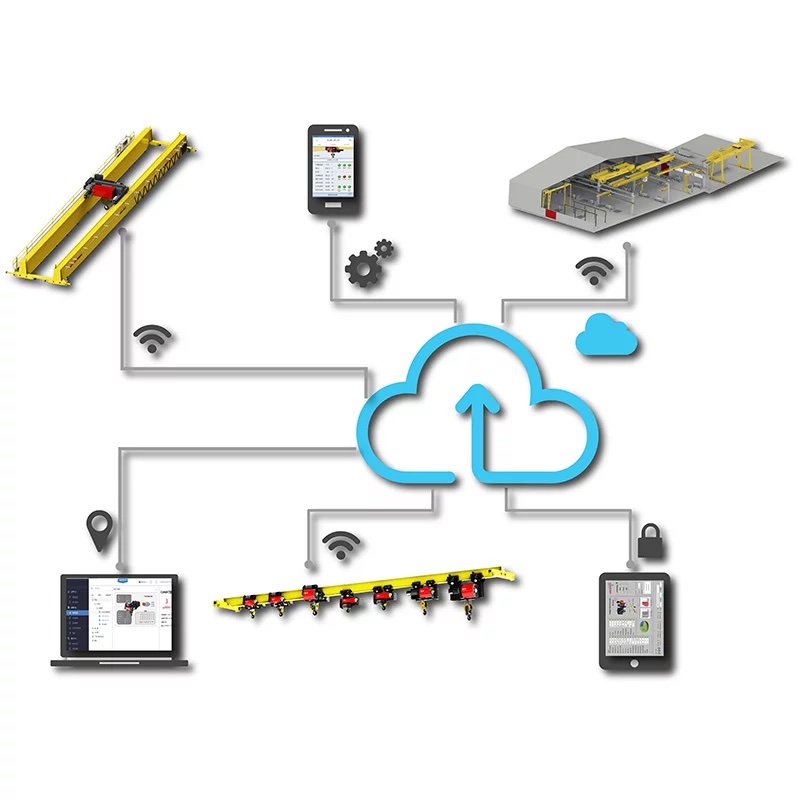
Remote Monitoring App: My Crane
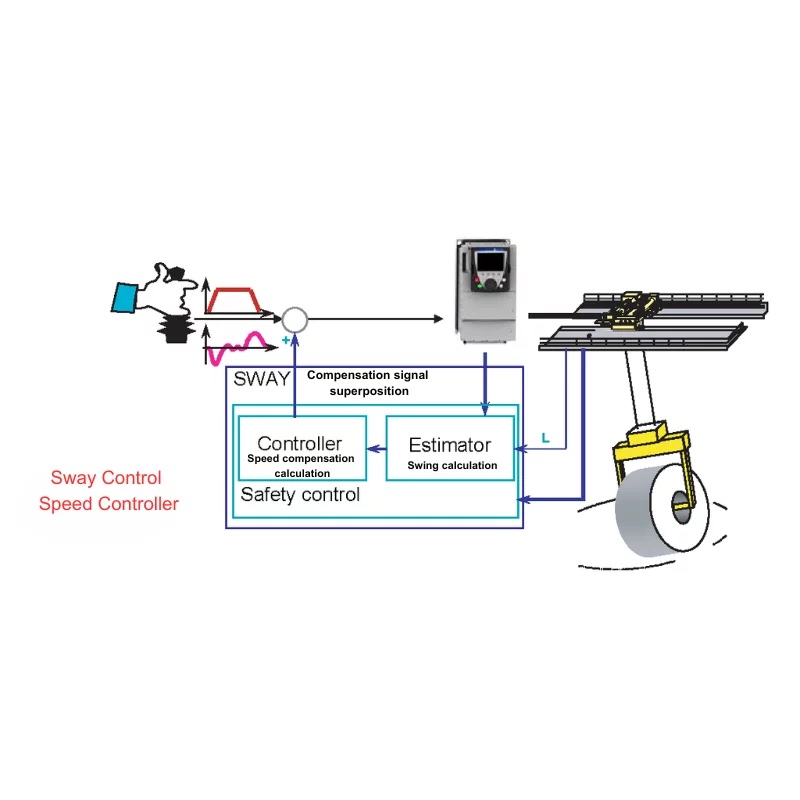
Sway Control
Based on the principle of motion compensation, it reduces swinging by over 90%.
When the operator issues a command, the electronic sway control system monitors the pendulum length and initial speed in real-time. It then calculates the synthesized speed for swing suppression according to a pre-set mathematical model and sends it to the inverter, thereby achieving the sway control and making the operation safer.
Inching
When the load approaches its destination, the crane moves it precisely by a pre-set micro-distance and automatically stops.
During each operation, the hook lifts or lowers the load by a small predetermined distance (ranging from 2 to 100 mm).
For example, if the inching micro-distance is set to 2 mm, the load will rise or descend by exactly 2 mm in each step and then stop automatically. This ensures the safe and precise positioning of the load.
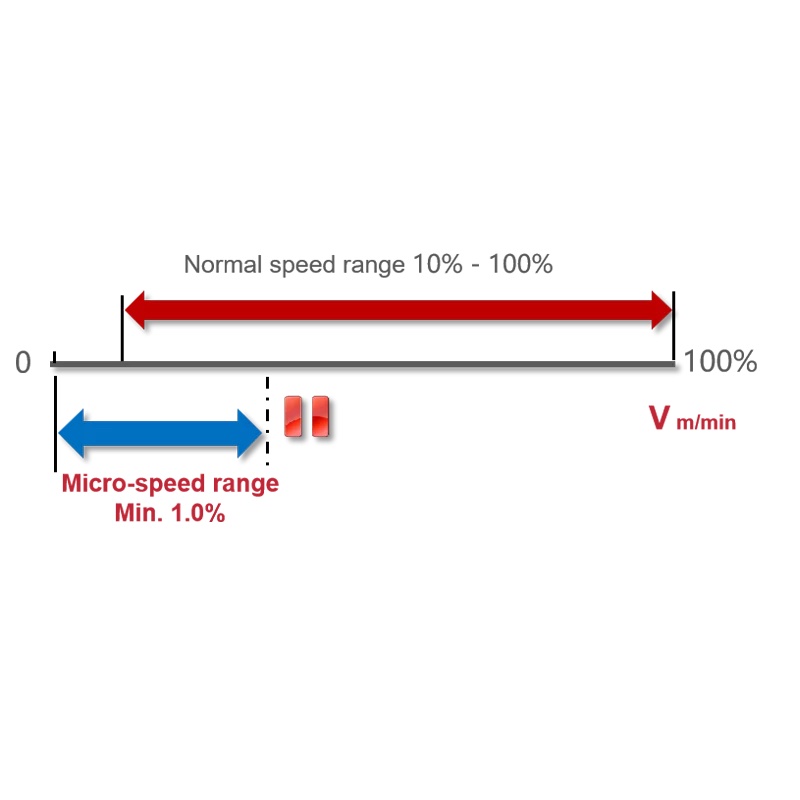
Micro Speed
The rated maximum speed is reduced to a desired limited speed to allow for precise control of the load’s movement speed.
The micro-speed range can be set between 1% and 99% of the rated speed.
For example, if the rated speed is 0-5 m/min and the micro-speed is set at 30%, the load will move within the speed range of 0.05-1.5 m/min. This avoids rapid movement of the load, ensures precise positioning, protects valuable items, and enhances safety.
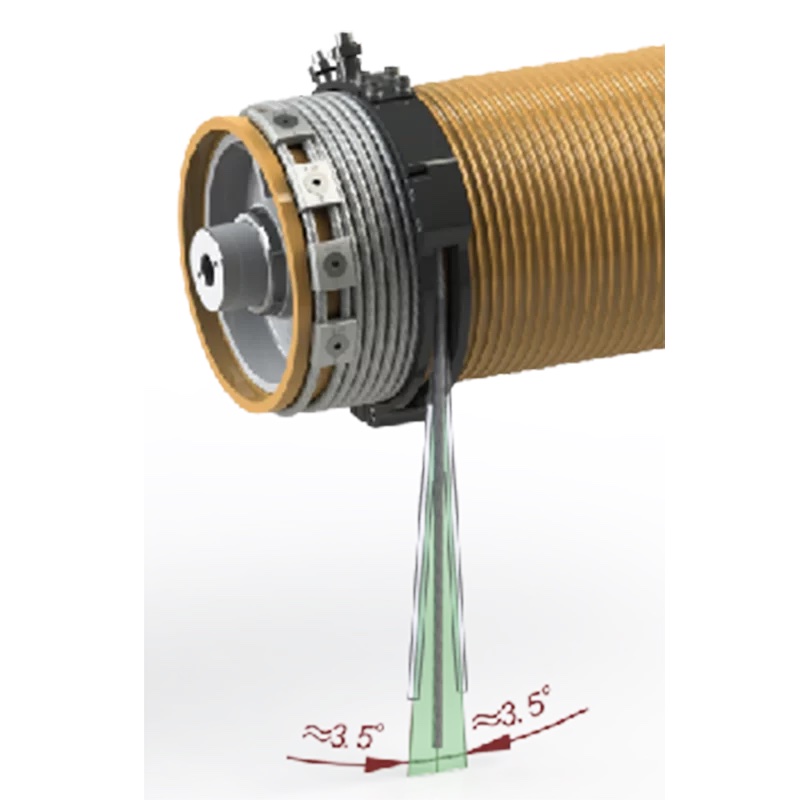
Side Pull Prevention
When the lifting angle exceeds the preset safe range, the lifting operation stops immediately to prevent oblique lifting. However, the load can still be lowered at this point.
The design allows a side pull angle of ±3.5°, which prevents risks such as wire rope damage and guide rope rupture caused by improper load suspension methods.
ABS
Through real-time monitoring, if the system detects that the brake pads are locked, the lifting motor is immediately powered off and stops running to prevent accidents such as brake pad burnout or load slipping.
This system features dual protection with a redundant design:
Electronic Anti-Lock Protection
When the safety monitor detects a sudden drop in braking current, it sends a signal indicating that the brake pads are locked, and the lifting motor is immediately powered off and stops.
Mechanical Anti-Lock Protection
Composed of adjustable mechanical contacts and microswitches, this system triggers the microswitch when the brake pads lock, causing the lifting motor to immediately power off and stop.
The Anti-Lock Braking System is suitable for frequent heavy-load applications, such as electromagnetic lifting, grab lifting, steel coil handling, paper roll handling, and stone material handling.
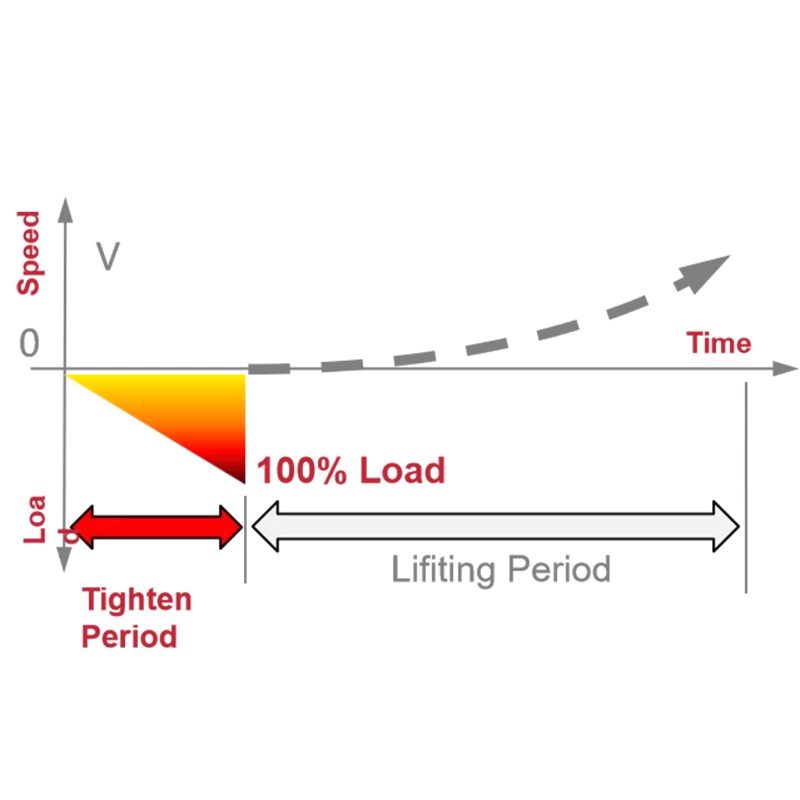
Shock Load Prevention
The crane monitors the load size and automatically calculates the hoisting acceleration required to eliminate shock, gradually applying the load until the heavy object is lifted without impact.
Based on the increment of tension, the crane automatically calculates the tightening phase, during which there is almost no lifting motion. Once the tension stabilizes, the hook begins to lift, preventing sudden large loads from impacting the crane and the building structure.
Zero Speed Holding
During the brief period when the speed decreases to zero but the brake has not yet engaged, the motor continues to output full torque, ensuring that the load remains suspended without dropping. This facilitates quick reverse startup.
The holding time ranges from 3 to 5 seconds. This function prevents the load from falling, enhances safety, reduces reverse startup time, minimizes impact, improves production efficiency, and extends the service life of the brake and crane structure.
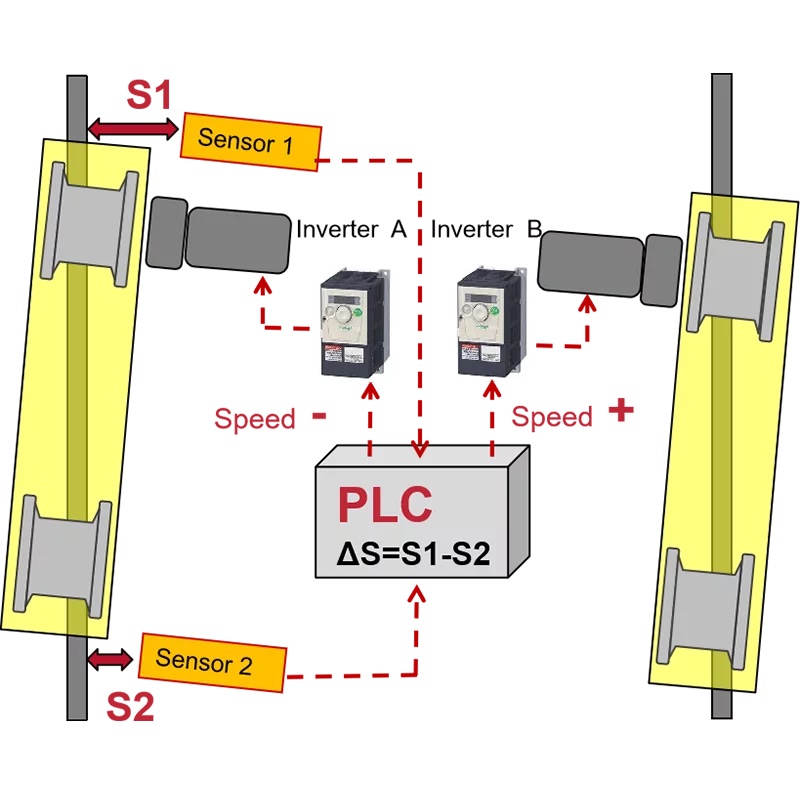
Off-track Correction
The off-track correction system automatically adjusts any deviation from the track, ensuring that the equipment always operates on the correct path.
The system is composed of a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), sensors, and an inverter. Sensors at both ends of the end carriage continuously monitor distances S1 and S2 in real-time and transmit these values to the PLC. The PLC calculates the difference ΔS = S1 – S2.
If ΔS exceeds the allowable tolerance, the PLC automatically generates a speed compensation value and sends it to the inverter, which adjusts the motor speed accordingly. This involves accelerating the lagging side while decelerating the leading side, thereby achieving precise correction of the deviation.
This function ensures smooth and accurate operation, reducing wear on the equipment and enhancing overall safety and efficiency.
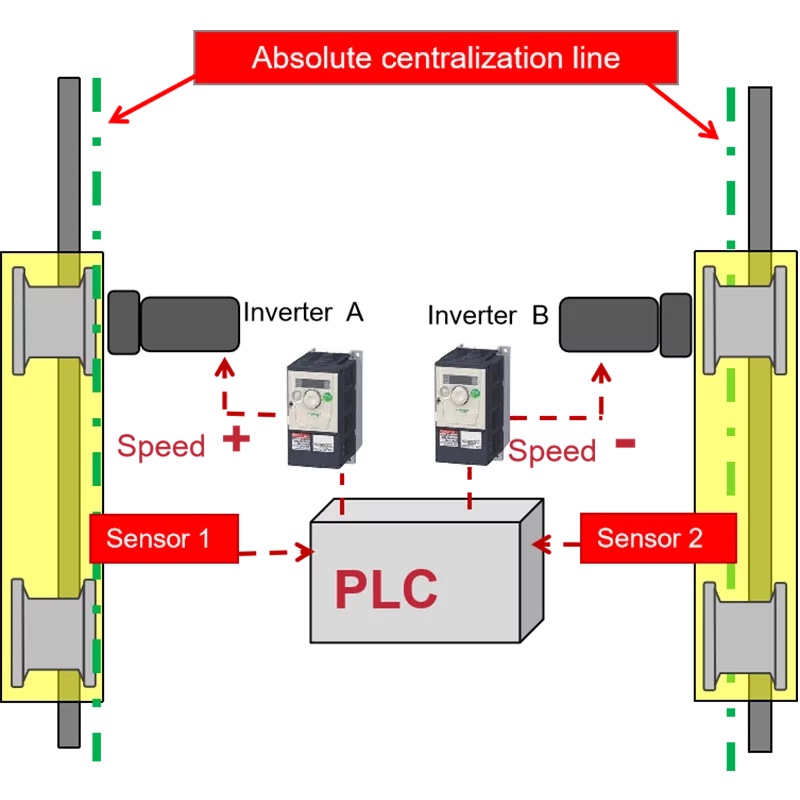
Track Centering
The track centering system automatically adjusts the position of the end carriage to ensure that the crane operates precisely along the absolute centerline.
The system is composed of sensors, a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), and an inverter. Sensors on each side of the end carriage continuously monitor any deviation from the absolute center reference line in real-time and provide feedback to the PLC.
If a deviation is detected, the PLC automatically generates a speed compensation value and transmits it to the inverter, which adjusts the motor speed accordingly. This involves accelerating the outer side while decelerating the inner side, thereby achieving precise alignment and maintaining the crane’s central position.
This function ensures stable operation, reduces mechanical stress, and enhances operational safety and efficiency.
My Crane App
Real-Time Monitoring: Check the operational status of your crane at any time via the mobile app, including key parameters such as load conditions, working hours, and motor temperature, giving you complete control over your equipment.
Alarm Notifications: When abnormalities occur or alarms are triggered, the system immediately sends notifications through the app, enabling users to respond quickly and resolve issues without delay.
Historical Data Analysis: Record and analyze historical operational data of your equipment to optimize workflows and develop scientifically sound maintenance plans.
Cloud Synchronization: All data is securely stored and backed up in the cloud, ensuring information safety and traceability while supporting access from multiple devices.